 Contract protectionFull worry free legal protection
Contract protectionFull worry free legal protection Certified MerchantProfessional certification
Certified MerchantProfessional certification Support 24/7Contact us 24 hours a day
Support 24/7Contact us 24 hours a day Payment SecureWe ensure secure payment
Payment SecureWe ensure secure payment
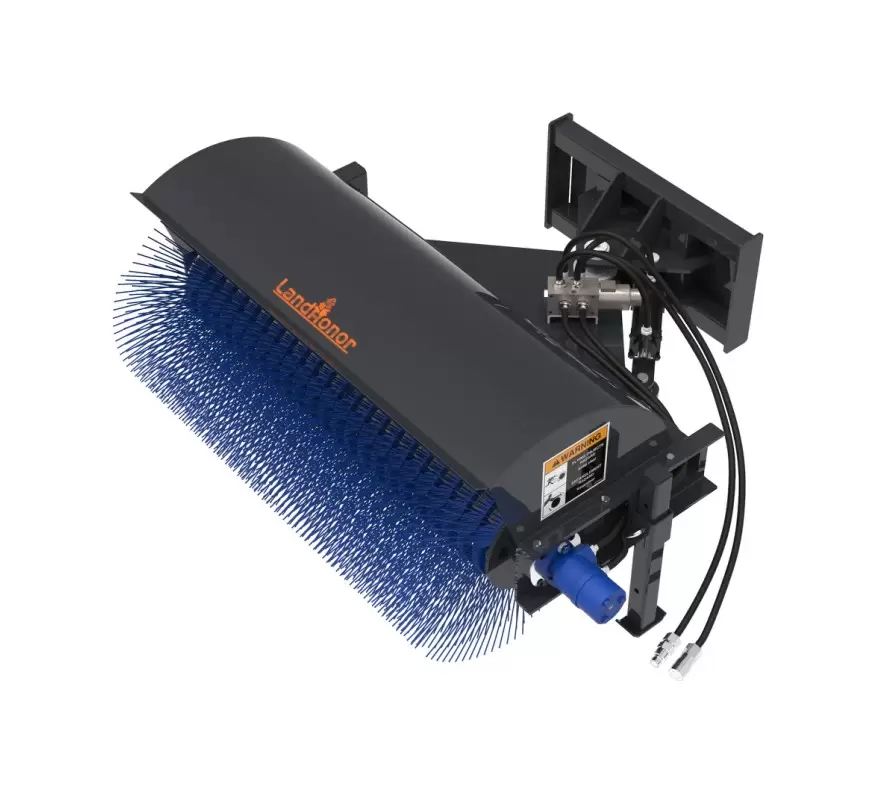
Hay Accumulator Grapple
Hay grabbers, often referred to as hay forks or hay grapples, are essential tools in modern agricultural practices, specifically designed for efficiently handling bales of hay and other bulk materials. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of their functionality, design, and best practices for use.
Design and Functionality
Hay grabbers are typically mounted on the front of tractors or skid steer loaders. Their primary components include:
Tines: These are the pronged extensions that penetrate and secure the hay. Tine design can vary, with options such as rigid, adjustable, or curved tines, each suited for different bale types and handling conditions.
Frame: The frame serves as the backbone of the grabber, providing structural integrity and housing the hydraulic or mechanical systems that operate the tines.
Hydraulic System: Most modern hay grabbers utilize hydraulic actuators for efficient operation. This system allows for smooth opening and closing of the tines, which is crucial for minimizing damage to the hay during handling.
Mounting Attachment: Various attachment types (e.g., quick-attach systems) facilitate easy connection to different machinery, enhancing versatility across different agricultural tasks.
Application Techniques
Efficient use of a hay grabber involves several key techniques:
Approach Angle: When approaching a stack of hay bales, maintain a low angle to reduce the risk of slippage. This angle also helps in penetrating the bales effectively without displacing them.
Controlled Engagement: Gradually engage the tines into the hay. Avoid aggressive thrusting, as this may damage both the equipment and the hay, resulting in waste.
Load Management: Ensure that the grabber is not overloaded. Exceeding the recommended weight limits can strain the hydraulic system and lead to premature wear or equipment failure.
Transporting Bales: When transporting bales, maintain a low center of gravity by keeping the load close to the ground. This improves stability and reduces the risk of tipping over.
Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance is crucial for prolonging the lifespan of a hay grabber:
Regular Inspection: Frequently inspect tines for wear or bending. Damaged tines should be replaced promptly to ensure optimal performance.
Hydraulic Check: Monitor hydraulic fluid levels and inspect hoses for leaks. Regularly check hydraulic connections to prevent fluid loss and maintain pressure.
Cleaning: After use, clean the grabber to remove dirt and debris. This prevents rust and corrosion, especially in the hydraulic components.
Lubrication: Apply appropriate lubricants to moving parts and pivot points to ensure smooth operation and reduce friction.
Conclusion
Hay grabbers are indispensable tools in agricultural operations, providing efficiency and ease in handling hay bales. Understanding their design, optimal usage techniques, and maintenance practices ensures that operators can maximize productivity while minimizing equipment wear. By following these guidelines, farmers can effectively manage their hay resources and improve overall operational efficiency.




